How Blockchain Improves Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain for Traceable and Transparent Supply Chains
In the current global marketplace, supply chains are growing more intricate, making it challenging for companies to monitor products from their source to their distribution points. Ensuring transparency and trust is essential for maintaining quality, minimizing fraud, and fulfilling customer demands. Blockchain technology offers a dependable solution by establishing a secure and unchangeable digital record of each transaction throughout the supply chain. In this blog, we will discuss how blockchain can enhance visibility, improve operations, and foster trust among suppliers, manufacturers, and consumers.

What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed digital ledger that records transactions securely and transparently across multiple participants. Each entry is verified through cryptographic methods and consensus mechanisms, making the data tamper-proof and reliable.
A blockchain is like a magical diary on the internet.
- Everyone has the same copy of the diary.
- When something is written, nobody can erase it.
- New things are always added at the end, one page after another.
- If someone tries to cheat, everyone else’s diary shows the truth.
- It’s just a safe way to keep records so everyone can trust them.
Now for the more technical explanation:
Stored in linked cryptographic blocks across a peer-to-peer network, a blockchain is a dispersed, append-only ledger.
Transactions are verified by consensus (e.g., PoW, PoS), then arranged into blocks referencing the hash of the preceding block, rendering them immutable.
It guarantees tamper resistance, eliminates the need for a central power, and allows transparent, verifiable records, usually extended with smart contracts for programmable trust.
Where Does This Data Get Stored?
As in traditional methods or blockchain, we still have to store our data somewhere, and that’s definitely going to be in a database. But you might be wondering if the data is still stored in a DB. How does this prevent tampering? Satoshi Nakamoto thought exactly like that and created a system wherein data is stored throughout a network of computers linked by cryptographic hashes (as seen in the image: How Blockchain works), hence making it almost impossible to modify without everyone noticing.
The network rejects a record someone tries to delete on a blockchain since other nodes still hold the original copy, nearly eliminating tampering.
Where can blockchain actually be used?
Blockchain technology can be applied in almost every field, from payments and remittances to healthcare, real estate, NFTs, energy, and even supply chain management.
How to Use Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
To know how exactly the blockchain can help, first, let us know how the supply chain industry works so that you’ll get a better understanding.
A supply chain is like a journey things take — from being made to being sold to you.
For chocolate: Farm → Factory → Truck → Store → You.
Many stakeholders participate in a supply chain; thus, conventional approaches like Paper-Based Records, Spreadsheets, and Manual Data Entry, and Email and Phone Communication may make records open to manipulation.
Let’s walk through how blockchain fits into each stage of the supply chain:
1. Product Creation / Origin
- Data Captured: Source location, raw material details, production date.
- Action: Supplier uploads data to the blockchain via IoT devices, QR/RFID scans, or manual entry.
- Result: First block for this product/batch is created.
2. Manufacturing / Processing
- Data Captured: Factory location, processing details, quality checks, certifications.
- Action: Manufacturer adds a new transaction to the blockchain, linking it to the product’s initial block.
- Result: Consumers and partners can verify authenticity and compliance.
3. Packaging & Shipping
- Data Captured: Packaging details, batch numbers, shipping dates, and GPS coordinates.
- Action: Logistics provider updates blockchain with real-time transport data.
- Result: Everyone in the network can see where the goods are in real time.
4. Customs / Regulatory Checks (If Applicable)
- Data Captured: Import/export documents, inspection approvals.
- Action: Customs officers add verification entries directly to the blockchain.
- Result: Fraud and delays are reduced because all documents are verifiable instantly.
5. Warehousing & Distributiong
- Data Captured: includes place, humidity, storage conditions, and handling history.
- Action: Blockchain updates warehouses when goods are received, stored, and transported out.
- Result: Keeps a continuous chain of custody.
6. Retail / End Consumer
- Data Captured: Arrival date, store details, shelf life, and sale transaction.
- Action: Retailer records final product entry. Consumers can scan QR/NFC to see full history.
- Result: Full transparency from farm/factory to shelf.
7. Returns / Recalls (If Needed)
- Action: Identify affected batches instantly through blockchain data.
- Result: Targeted recalls instead of pulling all products, saving cost and waste.
Here is a table comparing Traditional methods vs Blockchain-based methods:
| Aspect | Traditional Methods | Blockchain-Based Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Record Storage | Paper documents, spreadsheets, isolated ERP systems | Distributed ledger shared across all stakeholders |
| Data Integrity | Can be altered or deleted without detection | Immutable once added, records cannot be changed |
| Transparency | Limited each party maintains its own records | Full visibility for authorized participants |
| Trust | Relies on central authority or mutual trust | Trustless verification through consensus |
| Data Access | Controlled by whoever owns the system | Shared access with role-based permissions |
| Verification | Manual checks and audits | Automated, cryptographic verification |
| Speed of Traceability | Slow days or weeks to trace issues | Fast seconds or minutes to trace any record |
| Error & Fraud Risk | Higher due to manual entry and isolated systems | Lower due to automation and immutable records |
| Integration | Often siloed, hard to connect systems | Can integrate IoT, sensors, and ERP in real time |
| Cost of Disputes | High lengthy investigations | Low - disputes resolved with verifiable history |
Real World Examples & Case Studies for Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
These are a few companies using Blockchain in their supply chain management.
Walmart - Tracking fresh produce and reducing food recall times.
Maersk & IBM - Global shipping visibility with TradeLens.
De Beers - Verifying diamond origin to avoid conflict diamonds.
Nestle - Tracking coffee bean origins for authenticity.
I can’t cover all the companies' case studies here for now, i'll just overview how Walmart uses blockchain on their supply chain.
Walmart - Tracking fresh produce and reducing food recall times
In 2016, Walmart tested its food traceability process by tracking sliced mangoes back to the source, and it took 6 days, 18 hours, and 26 minutes. Partnering with IBM and using Hyperledger Fabric, the same process now takes 2.2 seconds. This breakthrough has improved transparency, trust, and speed in tracing food items.
Walmart extended blockchain use to trace pork in China, collaborating with JD.com, IBM, and Tsinghua University to build a secure ledger for suppliers, shippers, and buyers. This set industry benchmarks for food safety and traceability.
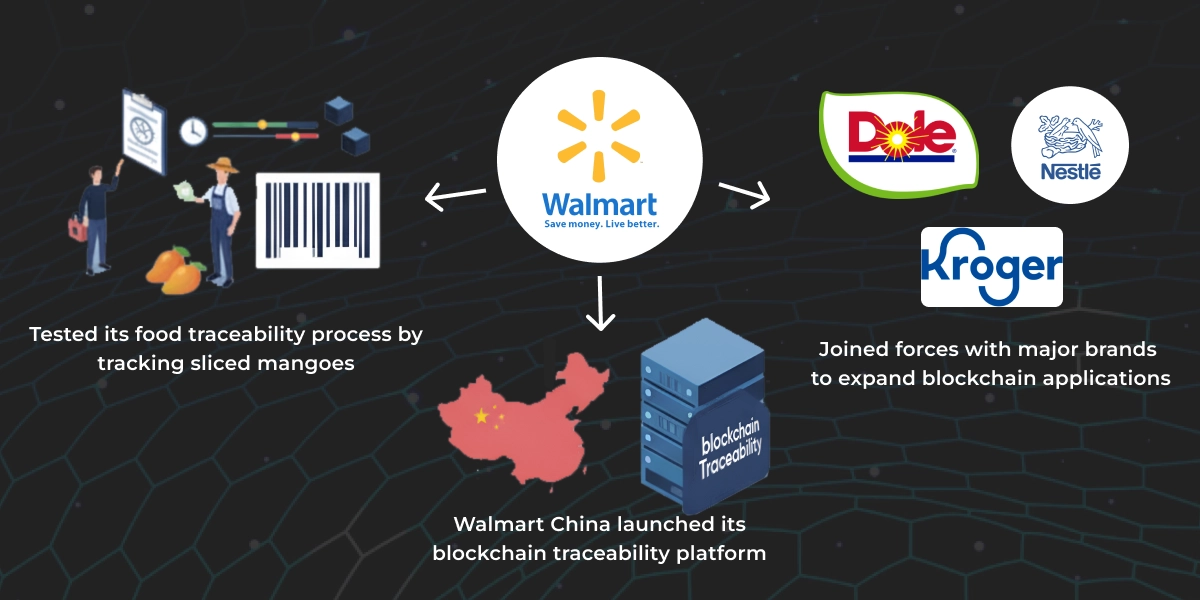
By 2017, Walmart joined forces with major brands like Nestlé, Dole, Kroger, Tyson Foods, and Unilever to expand blockchain applications. By 2018, they could trace over 25 products from mangoes to baby food back to farms within seconds. Suppliers of leafy greens were required to join IBM Food Trust, capturing and uploading standardized data like product IDs, lot codes, and harvest dates.
In 2019, Walmart China launched its blockchain traceability platform with VeChain and piloted shrimp tracking from farms in India to Sam’s Club USA, the first known blockchain tracking for shrimp exports.
Blockchain boosts transparency, accountability, and recall speed, helping reduce food waste and improve safety. Granular product data lets retailers better manage shelf life, quality checks, and supplier relations. Walmart continues to lead in blockchain-powered food safety innovation, proving it’s more than just tech; it’s a necessity for global food security.
Source https://tech.walmart.com/Beyond Transparency
Automated Payments with Smart Contracts
Think of smart contracts as self-running code on a shared ledger. When agreed conditions are met, for example, delivery confirmed via GPS, digital receipt, or IoT data, the payment triggers automatically. No chasing invoices or manual approvals.
Why it is great: It saves time, reduces mistakes, and ends most payment disputes.
Making Compliance
Easy-regulated industries drown in paperwork. With blockchain, inspection reports, test results, and certificates live as signed, tamper-evident records with role-based access and complete audit trails in one secure place.
Example: A pharmaceutical company uploads batch lab results; regulators check signatures and timestamps in seconds without email chains.
Why it is great: Less paperwork, quicker audits, and a near-zero chance of missing papers explain its excellence.
Tracking Sustainability Efforts
Customers and regulators want verifiable impact. Record emissions, water use, and sourcing at every step, link metrics to specific lots, and stream device data for trustworthy product passports and ESG reports.
Example: A fashion brand traces organic cotton farm to store, attaching verified chemistry, energy, and transport data at each handoff.
Why it is great: It inspires trust, makes a case for sustainability, and presents facts of measurable improvements.
Challenges & Limitations
There are actual challenges with the mighty technologies. Application of blockchain in supply chains requires coordination, integration effort, and a change in operations among and between a set of stakeholders.
High Setup cost
Building and integrating blockchain systems isn’t cheap, especially in the beginning. It often requires new tech, staff training, and system upgrades. Starting from Cloud Infra, IoT Sensors, Secure gateways, Blockchain platform setup, Custom APIs to integrate blockchain with existing ERP, Data migration tools, Training employees, Educating supply chain partners, Creating new operational workflows, Implementing identity and access management systems, and beyond.
Data input accuracy (blockchain can’t fix human entry errors)
Data is important when it comes to technology, especially when it comes to blockchain. There should be no human errors because once we enter the data onto the network, it can never be modified, as we explained earlier in the blockchain explanation.
Future Trends in Blockchain Supply Chain Innovation
Blockchain continues to reshape supply chain management, driven by new technological integrations, expanding use cases, and global demands for transparency, efficiency, and sustainability. Think about it, Blockchain itself is an advanced and safe platform; integrating Blockchain with AI will open up a whole new opportunity and achieve a technical pinnacle. These are a few points of future trends in the blockchain supply chain.
Blockchain integrated with AI
Integrating AI with a vast and reliable blockchain can greatly boost AI’s capabilities, enabling highly accurate predictive analysis.
IoT + Blockchain for Real-Time Condition Monitoring
Imagine combining smart sensors with blockchain. IoT devices — like GPS trackers or temperature and humidity sensors can send live updates straight to a blockchain while goods are being transported or stored.
For example, think of a refrigerated truck carrying vaccines. Sensors check the temperature every minute, and if it goes outside the safe range, the blockchain records it instantly and sends an alert.
Tokenization of Goods for Faster Trade Financing
Think of tokenization as giving physical goods a digital twin. Each item or shipment is turned into a digital token on the blockchain that proves ownership of that asset.
For example, a shipment of coffee beans could be represented by a token. The buyer doesn’t have to wait until the beans arrive — they can use that token as collateral to secure financing right away.
Expert Blockchain Solutions for Transparent Supply Chains
Blockchain delivers supply chain transparency, automated payments with smart contracts, trusted traceability, and strong data integrity across IoT and AI-driven networks. It streamlines compliance and proves sustainability without friction. Embrace tokenization and modern governance to scale confidently. Inklidox, a reliable team of young tech experts, implements these blockchain solutions for supply chain transparency & traceability seamlessly.

